
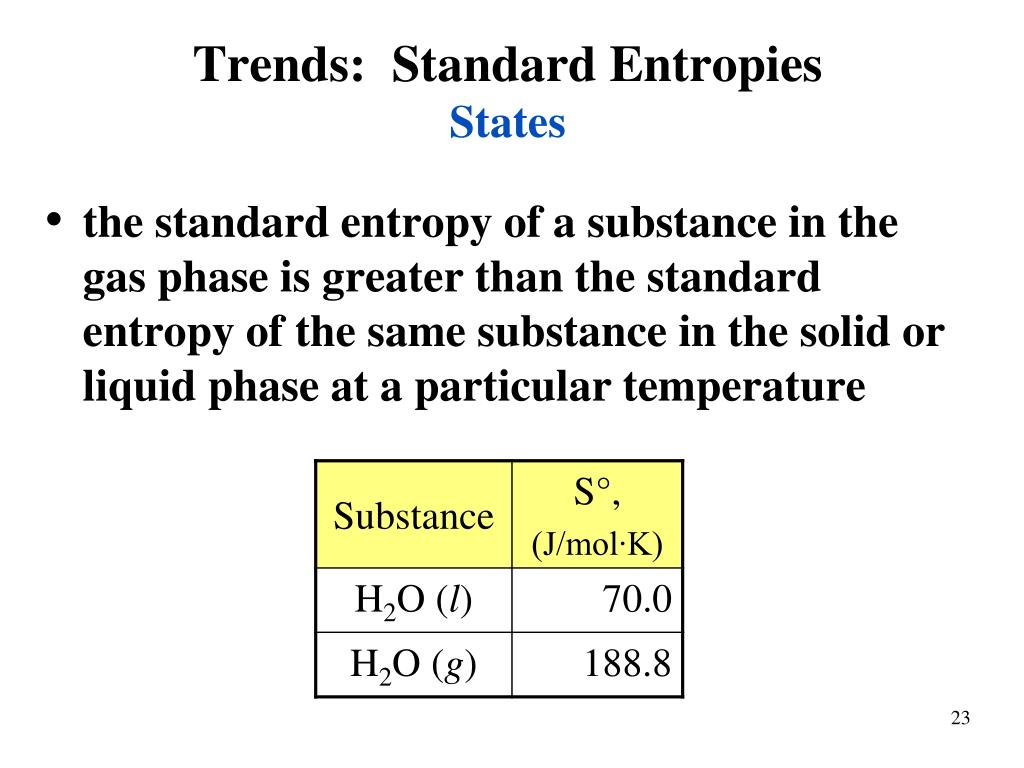
Therefore, the order is: Hexane > Cyclohexane > Benzene.Īll of the chemicals listed are phosphorus halides: PF 2 Cl 3, PF 3 and PF 5. So, the compound is arranged in decreasing order of standard molar entropy as: The electron delocalization around the molecule causes the molecule to deform. It's also well knowledge that benzene is a relatively stable chemical. The cyclohexane would thus have a larger molar entropy than the benzene.
There are 6 + 12 = 18 atoms in cyclohexane.Īs a result, because hexane has the most atoms, it will have the most potential vibration modes and the biggest molar mass entropy. There are a total of 6 + 6 = 12 atoms in benzene. As a result, in each scenario, the total number of atoms should be evaluated. In this example, however, all molecules contain a chain of six C atoms, with a varied number of H atoms linked depending on the structure. The more atoms or the longer the chain, the more vibration modes are conceivable. We can compare molecular complexity as the defining factor for entropy difference if the physical condition of all compounds is the same - liquid (at ambient temperature and pressure).ĭue to the mobility of distinct sections of a molecule, bigger compounds have a higher entropy. The metals are arranged in decreasing order of standard molar entropy as:Īll of the chemicals listed are hydrocarbons: hexane C 6 H 14, benzene C 6 H 6, and cyclohexane C 6 H 12. Due to the same reasoning, Calcium would have a larger molar entropy than Magnesium. As a result, the Ba has the highest molar entropy. The energy levels for larger, heavier atoms move closer within a periodic group, implying that the number of microstates and molar entropy increase. In the Periodic Table, all metals are found in Group in the following order: 
The 56th element in the periodic table is barium ( Ba 56 ).

Calcium Ca 20 is the periodic table's 20th element.In the periodic table, magnesium ( Mg 12 ) is the 12th element.The number of atoms in each compound is counted as follows: The more electrons an atom possesses, the more electrons it has delocalized in the lattice, resulting in a higher entropy. As a result, we must consider the atomic number (and weight) of each metal when comparing entropy. Only metals are considered in this example, which all form metallic lattices with delocalized electrons. We may compare molecular complexity as the defining factor for entropy difference since all compounds have the same physical state - solid (at the given temperature and pressure).ĭue to the mobility of distinct sections of a molecule, bigger compounds have a higher entropy. All of the compounds - Mg, Ca, and Ba - are metals of some sort.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
